Tutorial 1: Rabi Oscillations
In this tutorial, you will learn how to manipulate the state of a single neutral atom. This is the “Hello World” of quantum computing, demonstrating coherent control over a qubit.
1. The Physics: What are Rabi Oscillations?
Section titled “1. The Physics: What are Rabi Oscillations?”By shining a constant laser light on an atom at a specific amplitude Ω, the qubit’s state oscillates periodically between its ground state (0) and its excited Rydberg state (r). This oscillation happens at frequency Ω/2π, Ω is therefore named the Rabi frequency.
-
At 𝑡 = 0: the atom is in the ground state (0). If you measure it 1000 times, you will always get 0.
-
At 𝑡 = π/Ω: the atom reaches its maximum probability of being in the Rydberg state. If you measure it 1000 times, you will always get 1
-
At 𝑡 = π/(2Ω): the atom stops mid-oscillation, forming a balanced superposition of the two states. If you measure the atom 1000 times, you should get 500 times 0 and 500 times 1.
Let’s modify the state of one atom to have it in superposition of the ground and rydberg state !
2. Step-by-Step Implementation
Section titled “2. Step-by-Step Implementation”-
Set up the Register
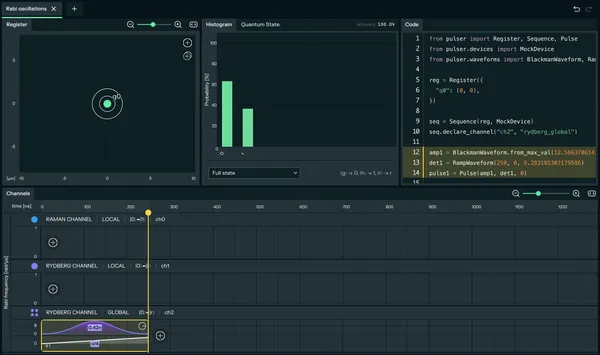
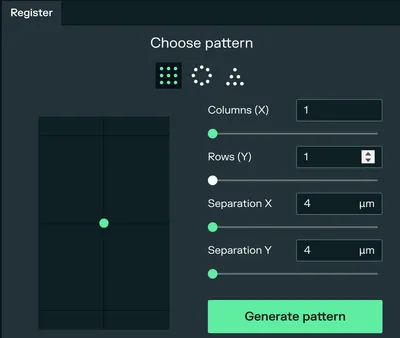
After creating a new experiment, go to the Register tab. Create a column and a row with a single atom, then click on generate pattern. This atom will be our qubit.
-
Channel Selection
By default, there are already 3 channels created :
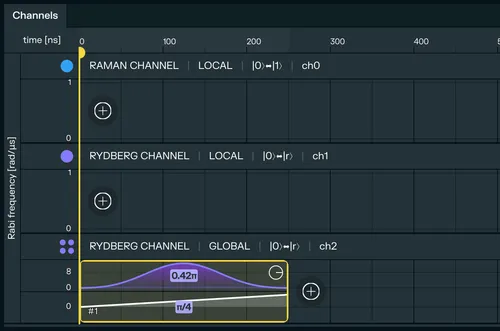
RAMAN CHANNEL | LOCAL,RYDBERG CHANNEL | LOCALandRYDBERG CHANNEL | GLOBAL, but you can create, delete or update the channels if you need to on the right panel. In the Channels timeline at the bottom, identify theRYDBERG CHANNEL | GLOBAL. This channel allows us to excite atoms to their Rydberg state using a laser that covers the entire register.
-
Create the Pulse
Add a pulse to the timeline by clicking the (+) button on the Rydberg Global row.
-
Configure the Pulse Settings
When you create a pulse, the Pulse Tab opens on the right. For this tutorial, we will use the default settings, that provide the pulses with the highest fidelity :
- Amplitude Waveform:
Blackmanis selected by default. This bell-shaped curve helps minimize unwanted transitions. - Max Value: Set to 4 π rad/µs to ensure strong driving.
- Detuning Waveform: Set to
Constantwith value 0 π rad/µs (resonance). - Duration: Set to 250 ns.
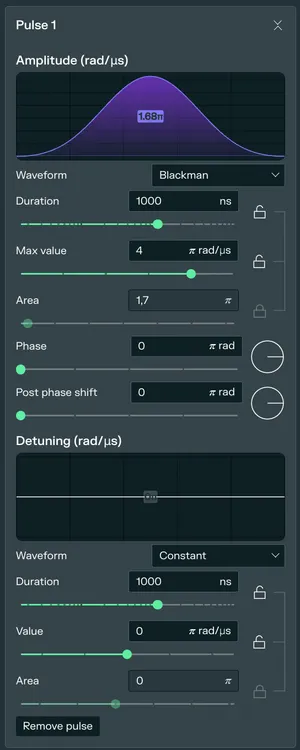
- Amplitude Waveform:
-
Visualize and Run
Now that you have designed the pulse, you should see the purple bell-shaped pulse and the white detuning ramp in your timeline.
You should be on the Local Emulation tab on the right panel. Since there is only one atom in the register the emulation will be instantaneous, you can now press the Play button to run the simulation.
The histogram and state evolution will show you the probability of the atom being in the excited state. You have just performed a fundamental quantum operation: you have modified the state of your atom to be in a superposition of the ground and rydberg state !